Automation Engineers in 2025: Powering Efficiency and Innovation in the AI Revolution
In the rapidly evolving world of technology, automation engineers stand as key architects of efficiency. These professionals design, develop, and deploy automated systems that optimize business operations, IT workflows, and development pipelines. As AI adoption skyrockets, the demand for automation engineers has surged, making this a pivotal career in addressing modern enterprise needs.
Recent data highlights the boom: Private AI investments in the US reached over $109 billion in 2025, far outpacing global competitors. Generative AI investments alone climbed to $33.9 billion worldwide, up 18.7% from the prior year. With 78% of organizations leveraging AI in 2024—a jump from 55%—automation is no longer optional but essential.
Though concerns about job automation persist, its integration across industries like healthcare, finance, and IT is irreversible. Automation engineers are crucial in managing this shift, ensuring seamless implementation and oversight.
Defining the automation engineer position
While automation has roots in manufacturing, its application in non-industrial sectors is expanding. In IT, emphasis is on service automation and quality assurance testing. Automation engineers focus on eradicating inefficiencies, bugs, and errors in software, products, and service delivery.
They engineer solutions like automated chatbots for customer queries, streamlined IT ticketing, and faster software releases with minimal defects. By automating repetitive tasks, they enhance reliability, reduce human workload, and boost overall productivity.
Core duties and responsibilities
Automation engineers in IT craft solutions to elevate software performance and system maintenance. They collaborate with teams to identify issues, gather specifications, and automate processes across hardware, software, or operations.
Common tasks include:
- Pinpointing automation opportunities in workflows.
- Developing and conducting QA tests with automated scripts.
- Testing components like databases, networks, applications, and hardware.
- Spotting and resolving bugs in development or services.
- Deploying relevant automation software and databases.
- Working with cross-functional teams to enhance processes.
- Collecting stakeholder feedback for tailored solutions.
Responsibilities adapt by sector, but the core is efficiency-driven innovation.
AI’s role in automation engineering
Automation predates AI, originating from industrial-era machinery. Today, AI supercharges it with predictive analytics and intelligent decision-making.
AI minimizes errors, handles vast data, and accelerates coding and troubleshooting. It automates QA segments and fixes minor issues independently, hastening market delivery. Yet, human engineers remain indispensable for navigating intricate systems and creative problem-solving.
Salary expectations for automation engineers in 2025
The field offers robust compensation. In the US, average salaries hover around $116,319 annually, with ranges from $92,000 to $148,000. Senior positions can reach $127,895 or more.
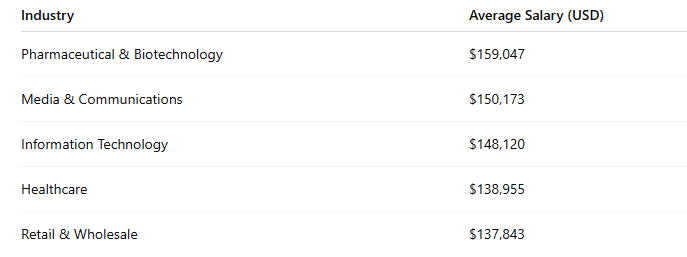
Location example:
Average salary in New York City → $123,601
Essential skills for success
Thriving requires technical depth and soft skills. Proficiency in programming (e.g., C#, SQL, Java), operating systems, robotics, AI, and machine learning is vital. Knowledge of Agile, DevOps, and cloud tech is standard.
Soft skills—communication, collaboration, problem-solving, leadership, and project management—enable effective cross-team work.
Pathway to becoming an automation engineer
Begin with a bachelor’s in computer science or engineering, emphasizing robotics, AI, statistics, and neural networks. Advanced roles may need a master’s or testing experience.
Tailor skills to industries by reviewing job listings.
Variations in automation engineering roles
Beyond QA automation, titles include:
- Automation Design Engineer
- Automation Systems Engineer
- Automation Specialist
- Selenium Automation Engineer
- Cloud Automation Engineer
- Test Automation Engineer
- End-to-End Automation Engineer
Focus areas range from cloud to specific tools.
Top tools for automation engineers
Automated testing tools are foundational for QA integration and reporting. Leading options in 2025:
- Tricentis Tosca
- TestGrid
- Selenium
- Playwright
- Cucumber
- Rainforest QA
- Testsigma
- BrowserStack
These enable efficient testing and issue resolution.
Valuable certifications to pursue
Certifications validate expertise in this emerging field:
- ISTQB Test Automation Engineer
- ISA Certified Automation Professional (CAP)
- UiPath AI and Process Automation
- Automation Anywhere Certifications
- Cisco Network Automation Engineer
- ISTQB Advanced Level Test Automation Engineer
These boost credibility and career prospects.
As automation reshapes industries, engineers in this space are poised for impact. Whether entering the field or advancing, embracing AI and continuous learning is key.
Our services:
- Staffing: Contract, contract-to-hire, direct hire, remote global hiring, SOW projects, and managed services.
- Remote hiring: Hire full-time IT professionals from our India-based talent network.
- Custom software development: Web/Mobile Development, UI/UX Design, QA & Automation, API Integration, DevOps, and Product Development.
Our products:
- ZenBasket: A customizable ecommerce platform.
- Zenyo payroll: Automated payroll processing for India.
- Zenyo workforce: Streamlined HR and productivity tools.
Services
Send Us Email
contact@centizen.com
Centizen
A Leading Staffing, Custom Software and SaaS Product Development company founded in 2003. We offer a wide range of scalable, innovative IT Staffing and Software Development Solutions.
Call Us
India: +91 63807-80156
USA & Canada: +1 (971) 420-1700
Send Us Email
contact@centizen.com
Centizen
A Leading Staffing, Custom Software and SaaS Product Development company founded in 2003. We offer a wide range of scalable, innovative IT Staffing and Software Development Solutions.
Call Us
India: +91 63807-80156
USA & Canada: +1 (971) 420-1700
Send Us Email
contact@centizen.com






